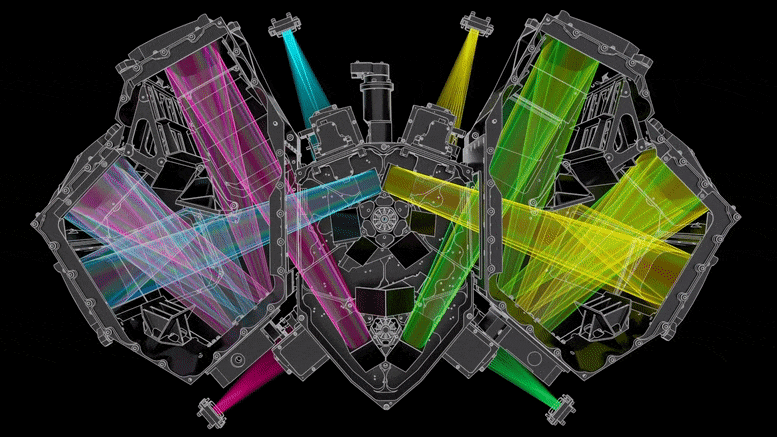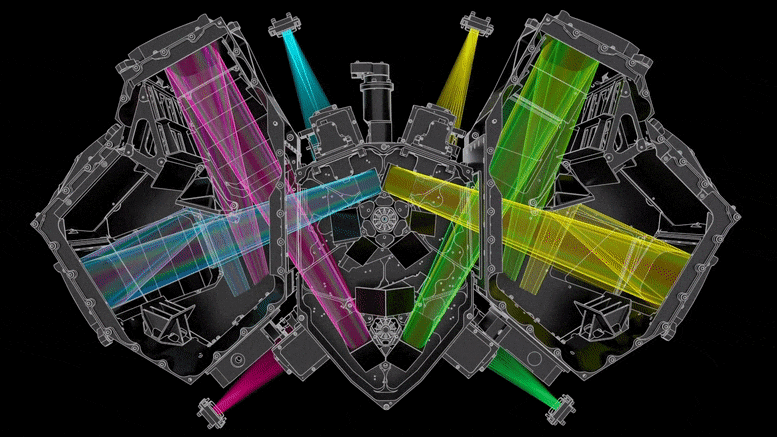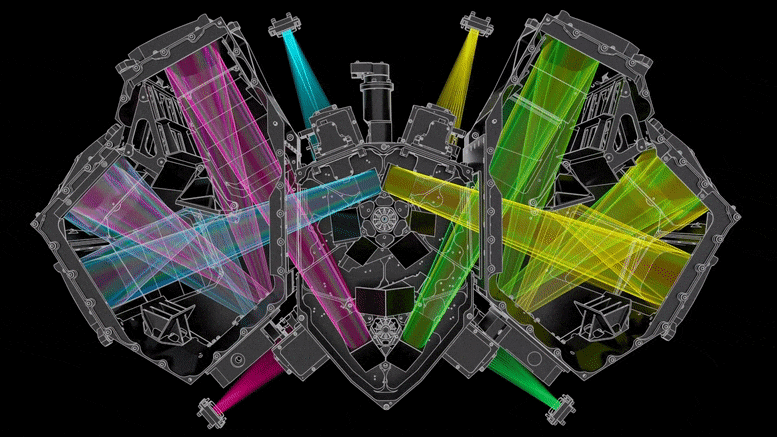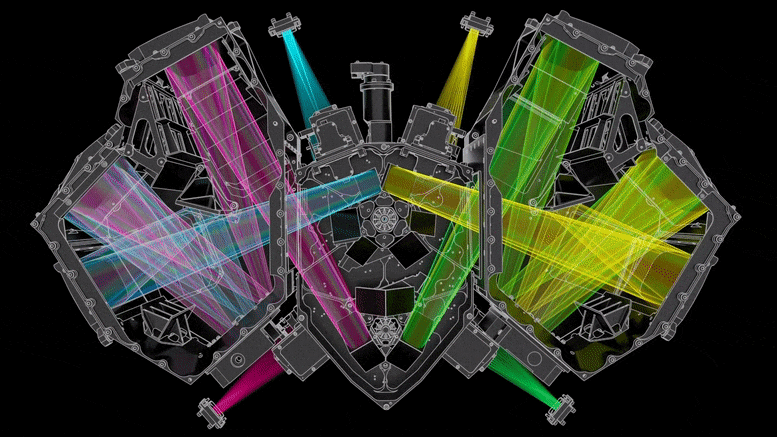

Ez az ábra a Webb teleszkóp hideg oldalát mutatja, ahol a tükrök és a műszerek találhatók. hitel: Northrop Grumman
Nemrég NIRISS, az egyik[{” attribute=””>NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope’s four primary scientific instruments concluded its postlaunch preparations and was declared ready for science. Now a second of Webb’s four primary scientific instruments, known as the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), has also concluded its postlaunch preparations and is now ready for science.
“We are thrilled that MIRI is now a functioning, state-of-the-art instrument with performances across all its capabilities better than expected.” — Gillian Wright and George Rieke
MIRI’s coronagraphic imaging capability, which uses two different styles of masks to intentionally block starlight from hitting its sensors when attempting to make observations of the star’s orbiting planets, was the last MIRI mode to be checked off. These customized masks allow scientists to directly detect exoplanets and study dust disks around their host stars in a way that has never been done before.
Along with Webb’s three other instruments, MIRI initially cooled off in the shade of Webb’s tennis-court-size sunshield to about 90 kelvins (minus 298 degrees Fahrenheit, or minus 183 degrees Celsius). To perform its intended science meant dropping to less than 7 kelvins — just a few degrees above the lowest temperature matter can reach — by using an electrically powered cryocooler. These extreme operating temperatures allow for MIRI to deliver mid-infrared images and spectra with an unprecedented combination of sharpness and sensitivity.

Webb MIRI spectroscopy animation: The beam of light coming from the telescope is then shown in deep blue entering the instrument through the pick-off mirror located at the top of the instrument and acting like a periscope.
Then, a series of mirrors redirect the light toward the bottom of the instruments where a set of 4 spectroscopic modules are located. Once there, the beam of light is divided by optical elements called dichroics in 4 beams corresponding to different parts of the mid-infrared region. Each beam enters its own integral field unit; these components split and reformat the light from the whole field of view, ready to be dispersed into spectra. This requires the light to be folded, bounced and split many times, making this probably one of Webb’s most complex light paths.
To finish this amazing voyage, the light of each beam is dispersed by gratings, creating spectra that then projects on 2 MIRI detectors (2 beams per detector). An amazing feat of engineering! Credit: ESA/ATG medialab
“We are thrilled that MIRI is now a functioning, state-of-the-art instrument with performances across all its capabilities better than expected. Our multinational commissioning team has done a fantastic job getting MIRI ready in the space of just a few weeks. Now we celebrate all the people, scientists, engineers, managers, national agencies, European Space Agency (ESA), and NASA, who have made this instrument a reality as MIRI begins to explore the infrared universe in ways and to depths never achieved before,” said Gillian Wright, MIRI European principal investigator at the UK Astronomy Technology Center, and George Rieke, MIRI science lead at the University of Arizona. MIRI was developed as a partnership between NASA and ESA (European Space Agency), with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory leading the U.S. efforts and a multi-national consortium of European astronomical institutes contributing for ESA.
With NIRISS and MIRI postlaunch commissioning activities concluded, the Webb team will continue to focus on checking off the remaining two modes on its other instruments. NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, a partnership with ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA, will release its first full-color images and spectroscopic data on July 12, 2022.

„Utazási specialista. Tipikus közösségi média tudós. Az állatok barátja mindenhol. Szabadúszó zombinindzsa. Twitter-barát.”





More Stories
A SpaceX Polaris Dawn űrszondájának legénysége a valaha volt legveszélyesebb űrsétára készül
Egy őskori tengeri tehenet evett meg egy krokodil és egy cápa a kövületek szerint
Egyforma dinoszaurusz-lábnyomokat fedeztek fel két kontinensen